- Article
Classification of SINE Tails in the Porcine Genome and Its Potential Impact on VWA8 Gene
- Yao Zheng,
- Shasha Shi and
- Chengyi Song
- + 8 authors
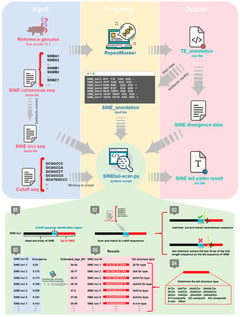
Background/Objectives: Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements (SINEs) constitute major components of mammalian genomes, but the structural diversity and evolutionary dynamics of their characteristic 3′ poly(A) tails have not been fully characterized. Methods: Based on the custom-developed SINEtail-scan pipeline, 1,018,332 SINEs with tail in the pig reference genome (Sus scrofa 11.1) were identified and systematically classified, revealing the diversity of tail sequence structures. According to nucleotide composition and microsatellite repeat patterns, the tail sequences were divided into 16 different structural types. Results: A-rich sequences predominated (66.3%), while non-A-rich tails exhibited characteristic architectures including AT-format, AC-format, and AG-format repeats. Temporal analysis spanning 85 million years demonstrated progressive tail modification, with A-rich proportions declining from 84.2% in recent insertions to 31.9% in ancient elements, accompanied by accumulation of complex non-A-rich structures. Comparative genomic analysis across 10 pig genome assemblies identified 308 SINE tail insertions within protein-coding sequences, of which 45 (14.6%) exhibited inter-individual structural polymorphism. Detailed investigation of a polymorphic insertion in the VWA8 gene revealed a 16-bp tail variant causing a frameshift mutation and C-terminal protein structure divergence. Conclusions: These findings establish SINE tail sequences as dynamic evolutionary substrates undergoing continuous modification through slippage-mediated mechanisms, with implications for genome evolution, population genetics, and gene function modulation in mammals.
7 February 2026